For these reasons, most companies use predetermined overhead rates rather than actual overhead rates in their cost accounting systems. A predetermined overhead rate is calculated at the start of the accounting period by dividing the estimated manufacturing overhead by the estimated activity base. The predetermined overhead rate is then applied to production to facilitate determining a standard cost for a product. Understanding predetermined overhead rates requires a solid grasp of foundational cost accounting principles. These concepts serve as the building blocks upon which the entire Bakery Accounting overhead allocation process rests. A clear understanding of these concepts is essential for accurately calculating and applying overhead costs to products or services.
Applying the Overhead Rate
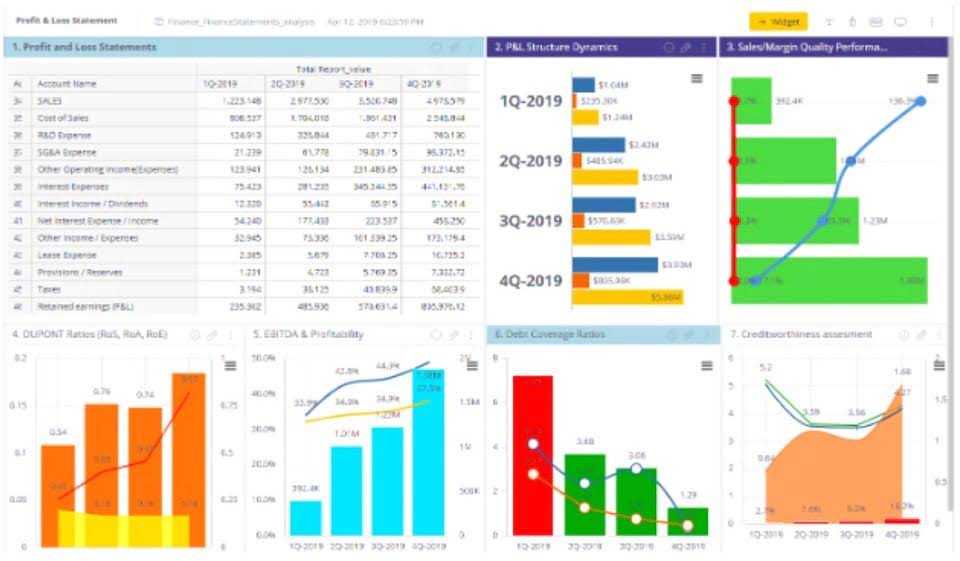
- When the $700,000 of overhead applied is divided by the estimated production of 140,000 units of the Solo product, the estimated overhead per product for the Solo product is $5.00 per unit.
- This option is best if you’re just starting out and don’t have any historical data to work with.
- Both figures are estimated and need to be estimated at the start of the project/period.
- The budgeted activity level is the expected level of production or activity that will be used to allocate overhead.
A predetermined overhead rate is a rate used to apply manufacturing overhead to products or job orders and is established before a period begins. This rate is calculated by dividing the estimated manufacturing overhead cost for a period by the estimated total units in the allocation base for that same period. A clear understanding of these concepts is essential for accurately calculating and applying overhead rates, leading to more informed decision-making and a more accurate assessment of product costs.
Choosing an Allocation Base
The controller acts as normal balance the overseer of the entire overhead allocation process, ensuring its accuracy, compliance, and alignment with the company’s financial reporting standards. This increases the value of inventory and reflects the allocation of overhead costs to production. The cost driver is the activity that is believed to drive or cause overhead costs to increase. The selection of a suitable cost driver, also known as an allocation base, is paramount to the accuracy of overhead allocation. It’s a completely estimated amount that changes with the change in the level of activity. The first step is to estimate total overheads to be incurred by the business.
Calculating the Predetermined Overhead Rate: A Comprehensive Guide
This allows businesses to capture the full cost of production in their accounting. One of the advantages of predetermined overhead rate is that businesses can use it to help with closing their books more quickly. This is because using this rate allows them to avoid compiling actual overhead costs as part of their closing process. Nonetheless, it is still essential for businesses to reconcile the difference between the actual overhead and the estimated overhead at the end of their fiscal year. Suppose that X limited produces a product X and uses labor hours to assign the manufacturing overhead cost. The estimated manufacturing overhead was $155,000, and the estimated labor hours involved were 1,200 hours.


He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University. This provides a more accurate representation of inventory values and cost of goods sold. The disposition of over- or under-applied overhead typically involves closing the balance to Cost of Goods Sold. This information can help you make decisions about where to cut costs or how to allocate your resources more efficiently. A good rule of thumb is to ask yourself if the cost will be incurred regardless of how much product you’re making.
- Calculating a predetermined overhead rate is one of the first tasks management will take on because it provides a formula to estimate the production costs of a product in advance.
- In this article, we will discuss the formula for predetermined overhead rate and how to calculate it.
- This encompasses a wide range of expenses, such as factory rent, utilities, depreciation on factory equipment, and the salaries of factory supervisors.
- Direct costs are costs directly tied to a product or service that a company produces.
- Here’s how a service-based business, namely a marketing agency, might go about calculating its predetermined overhead rate.
The Accounting Department: Guardians of Cost Allocation
A Predetermined Overhead rate shall be used to calculate an estimate on the projects that are yet to commence for overhead costs. It would involve calculating a known cost (like Labor cost) and then applying an overhead rate (which was predetermined) to this to project an unknown cost (which is the overhead amount). The formula for calculating Predetermined Overhead Rate is represented as follows. The estimated manufacturing overhead cost applied to the job during the accounting period will be 1,450. The estimated manufacturing overhead cost applied to the job during the accounting period will be 1,600. The estimated manufacturing overhead cost applied to the job during the accounting period will be 1,494.
This consolidates overhead cost information from multiple sources, including payroll, point-of-sale, billing and more. With a unified data set, generating financial statements and calculating accurate overhead rates is streamlined. If Department B has overhead costs of $30,000 but direct costs of $70,000, then its overhead rate is 43%. Despite having lower total overhead, Department B is less efficient since its overhead rate is higher. This $4 per DLH rate would then be used to apply overhead to production in the accounting period.
- The allocation of overhead to the cost of the product is also recognized in a systematic and rational manner.
- For this example, we’ll say the marketing agency estimates that it will work 2,500 hours in the upcoming year.
- The cost of your office rent would be considered overhead because it’s something you have to pay regardless of how many t-shirts you sell.
- The most prominent concern of this rate is that it is not realistic being that it is based on estimates.
- That is, a number of possible allocation bases such as direct labor hours, direct labor dollars, or machine hours can be used for the denominator of the predetermined overhead rate equation.
Direct Costs vs. the Overhead Rate
However, the use of multiple predetermined overhead rates also increases the amount of required accounting labor. This section provides a step-by-step guide to calculating and utilizing predetermined overhead rates, along with strategies for managing and improving overhead cost control. By leveraging the predetermined overhead rate insights derived from predetermined overhead rates, businesses can make more informed decisions, improve resource allocation, and ultimately enhance their overall financial performance.
